Contact Us
- Call Now:(01)773-455-6676
- Sales Email:sales@dedicatedhosting4u.com
- Support Email:support@dedicatedhosting4u.com
- Billing Email:billing@dedicatedhosting4u.com
Close Support
Raid backup server in depth
Raid backup server in depth
RAID is the short form of Redundant Array of Independent Disks. RAID refers to the way of combining different independent and small disks into single storage of large size. The disks which constitute this array are called the array members. To upgrade speed and performance, several physical disks integrate as one set to create Raid Backup Server. Different levels of RAID types: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
Different levels of RAID processing are –
RAID 0
It is the initial level to process. In a RAID 0, system data is written to disks in the array as different blocks. Enhance performance by using several disks at once. There are different controllers, one controller per disk, which helps to increase the performance. RAID-0 can combine two drives storage into a single volume. Linux, OS X, and Windows support RAID-0. The benefit of RAID 0 is that one disk failure does not affect the data of the second disk.
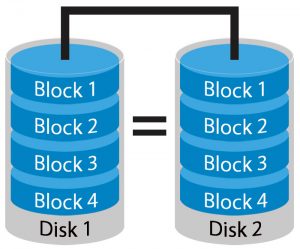
RAID 1
RAID-1 stores data in two drives, one is a data reader and the other one is a mirror drive. In case of failure of one drive, recover data using another drive and operate. We need a minimum of 2 drives for the RAID 1 array.
RAID 0+1
This is based on the combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. This level inherits RAID 0 performance and RAID 1 fault tolerance.
RAID 1E
This can survive the failure of 1 member disk or many numbers of non-adjacent disks. It uses both striping and mirroring techniques to store data in an array. There are 3 subtypes of the 1E layout.
- RAID 1E near: This creates on using only an odd number of disks. If the number of disks is even, then this turns to RAID 10.
- RAID 1E interleaved: Its implementation can be either by odd or even number of disks. IBM creates such controllers.
- RAID 1E far: Any number of disks can create RAID 1E far. This is similar to RAID 10. To recover such RAID, you should use a host protected area (HPA) to cut the half number of member disks and then recover RAID 0. This is because it is not possible to automatically recover configuration for RAID 1E far.
RAID 5
It is the regular level of the RAID process. In RAID 5 we need a minimum of 3 disks that can work for 16 blocks. The disks are divided into data blocks and every disk has an equal part of the data block written. The data is disbanding the overall drives of the raid backup server instead of writing on a single drive. The computer can determine the data from another block of the set in case of data unavailability. This means that the RAID 5 array supports single disk failure without any data loss. Although software identifies RAID-5 as a hardware controller. The extra cache to be aid for increasing the performance.
RAID 5E
This is one of the RAID 5 variations. In addition to RAID 5, RAID 5E has integrated share space to rebuild the array in case one member disks fail. The advantage of RAID 5E compared to RAID 5 is high read and write space with the dedicated drive. However, this leads to the complexity of rebuilding during member disk failure. We can create it using a standalone controller like the IBM ServeRAID controller.
Recovery of array parameters in RAID 5E is similar to RAID 5.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is equal to RAID 5 but the same data exists on two disks. This means to support 2 disks we need 4 disks. Unlike the RAID 5 in RAID 6, the array can survive on the second failure. In RAID 5 one disk fails, replacing it with a new one takes time, if another disk fails data may be lost forever.
RAID 10
The benefits of RAID 0 and RAID 1 can be a group to a single system. The mirroring of all data on secondary disks while using each disk set can speed up data transfers and also provides security. Several mirrors are created where the data is arranged in tapes on multiple disks, later extracted disk sets are mirrored. RAID 10 level has fault tolerance which is equal to RAID 1 with advancing read or write speeds on a single RAID 1 volume. In this RAID 10 level, the requirement is 4 disks.
RAID overview
For any business, data is the key resource. Data loss may result in business loss. Keep the regular backup to save some effort to access or to protect in case of drive failures. Using a raid backup server along with storage configurations can be an economical way to secure and access the data.
Characteristics of RAID
- It is fault-tolerant. This means even if one of the disks fails, it does not fail as a raid storage system. As there are multiple disks, the mean time between failure (MTBF) increases. If you redundantly store data, recovery becomes possible.
- Performance is much better than a single disk. The read and write speed of the array shows significant improvement.
- The capacity of RAID is the amount of user data onto the raid storage devices. This must not be always equal to the individual disk capacity of each of the disks.
- RAID gives a way to store similar data in various locations on many physical raid storage devices. This is known as ‘Redundant’.
RAID storage techniques
Following are the main techniques of storing data in a raid storage system :
- Striping: In this method, the data flow is fragmented into blocks of a certain size called block size. These blocks are then written across RAID one by one. This way of data storage increases performance. This makes RAID a good option in video editing systems.
- Mirroring: This is a storage technique where multiple copies of the same data are stored in different RAID members. a raid backup server improves fault tolerance as well as performance.
- Parity: In this technique, calculate a certain parity function for data blocks. In case of a drive failure, recalculate the missing block from the checksum which in turn improves fault tolerance.
All the existing RAID types are based on either of these three techniques and also a combination of the above.
RAID Implementations
Create RAID in the following ways:
Software RAID
This is the most inexpensive solution. This method uses operating system drivers. Most of the operating systems have an in-built capability to create many RAID levels. For example, the Windows operating system allows the user to create RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5.
Software RAID is create based on the user computer and so this uses the host CPU for implementation. In the case of RAID 0 and 1, the load on the CPU is negligible whereas, in the case of RAID types that are based on parity, 1 to 5 percent of CPU load is used depending on the number of disks. However, for practical purposes this is negligible.
Remember that there are some limitations to booting the system if you use software RAID. Only RAID 1 supports the boot partition, and it is impossible to system boot with software RAID 0 and 5. In most cases, software RAID does not implement hot swapping and so is not suitable where we require continuous availability.
Hardware RAID
Separate hardware is used for forming Hardware RAID. You can do this in one of the following ways:
- The RAID chip is design into a pretty economical motherboard.
- A more expensive option is using a standalone complex RAID controller. CPU supports these controllers and the battery build up cache memory.
Advantages of Hardware RAID over Software RAID
- CPU performance doesn’t affect it as it does not allow host computers.
- This allows the user to create boot partitions, unlike Software partitions.
- As communication with devices is direct, it improves error handling.
- It supports hot-swapping.
RAID 5 Recovery
The manual process to recover RAID 5 is too complex and time-consuming if you are not an expert. Using ReclaiMe Free Raid Recovery you can recover the drive much easier.
- Download the ReclaiMe Free Raid Recovery
- Using the Disks button, create an open disk image file of RAID 5 member disks.
- Select the available member disks and start RAID 5. You should have at least two of the disks. RAID 5 works even if one disk is missing.
- The RAID recovery finishes after the scan.
- After the RAID 5 configuration restores parameters, you should select one of the following:
- Run ReclaiMe data recovery software to recover data. This will launch in RAID recovery mode and display the partition on the raid backup server.
- You can save the recovered array parameters in a file in XML format. Also, you can open this file in ReclaiMe and start recovering data.
- You can also transfer the recovered parameters to some other data recovery tool you might want to use.
If you want to recover data manually, you have to determine the parity position and rotation to get the full configuration of your array. This is because like RAID 0, RAID 5 is a redundant array and stores parity data.
RAID 0 Recovery
RAID 0 can fail due to any of the following reasons:
- Failure of one or more RAID 0 member disks.
- Failure not associated with disk failure.
Member disk failure
As RAID 0 arrays are non-redundant, so if one of the disks on the raid storage system fails, data is lost forever. However, you can try to recover data from other member disks. You can only recover the files having a size smaller than (N-1) *(block size). If we store the file on the failed disk, we cannot recover data even if the file size is less than the above-mentioned threshold.
Other issues
Various other factors can also lead to RAID 0 failures. For example, operator error, controller error, or RAID 0 controlling software. In these cases, the configuration metadata is lost, but member disks work fine. With these failures, it is possible to recover data from RAID 0. Firstly, you determine the raid backup server configuration.
- Several member disks present.
- The order of the disks, which array was present in the first position.
- Block size
- Starting offset for the disks.
You can either opt for manual or software processes for RAID 0 recovery. The software process is similar to the RAID 5 recovery process using the software described above.
For manual recovery, you need to determine raid storage devices order manually. You can use log files with a timestamp for this purpose. Also, you need a disk viewer tool. Whenever a fragment of the suitable file is found on one of the member disks, this tool tracks which disk contains the next fragment and so on.
To determine the first disk, you can again use the disk viewer tool. Search the member disks for:
- The disk which contains the MBR in case of hardware RAID is the first disk.
- The disk which contains the boot sector at the beginning is the first disk in the case of software RAID.
For a hardware RAID 0, determine the block size by looking up possible values or checking in the manual for RAID-0 implementation. For example, Windows uses a 128 sector block for RAID 0.
On a hardware RAID 0, data mostly starts at the start of the hard drive. This is equivalent to setting the start offset of the member disk to 0. For a software RAID, the offsets are mostly identical. We can identify it by locating the volume sector.
Hot Swapping hard drive when RAID crashes
If there is no raid backup server downtime when RAID crashes and you need to change the raid backup drives. Then below is the process to swap hard drives when RAID crashes.
RAID 5 disk mirroring provides highly secure data protection in the event of failure. To create a RAID 5 array, you need 3 disks of similar capacity. RAID creates an exact copy on each of the raid backup drives and protects data in case of any of the drive failures. The usable capacity in RAID 5 is the disk size of the smallest drive. This is useful for personal and business purposes.
When the RAID operates in functional mode, the status is shown as Ready in ‘Storage Pools’.
In the event of a drive failure, you can check the drive status by the following steps:
- When a drive fails, the turbo NAS beeps for 1.5 sec.
- The status LED flashes Red continuously.
- In the storage Pool section, check the RAID group. The volume status shows in degraded mode.
To install a new drive to rebuild RAID 5, follow these steps:
- Prepare a new hard drive to rebuild the RAID configuration. The capacity of the new drive should be at least the same or more than the failed drive.
- Install the drive in Turbo NAS. It will beep at first. The status LED alternates between green and red.
- In the storage Pool section, the status shows as Rebuilding, and the progress bar is shown.
System logs contain the information of new disk volume.
Using RAID as a backup
RAID array can be used as a raid backup server with another backup software. If you have a Mac Pro with some external drives connected to it, you can connect the RAID array by Thunderbolt or USB 3. You can change the configuration of backup software so that it copies data to the RAID array.
A raid backup server offers extra protection for your backup over what you would have on a single drive. If any of the drives fails, device software will warn you and you can swap raid backup drives and this will ensure that your backups are reliable every time. This will prevent any occurrence of unreadable backup when your computer drive fails. However, using RAID alone as a backup might not be a good idea. Below are some of the problems you might encounter by using RAID as a backup alone:
- Suppose one day you find a corrupted file on your data server. According to the principle of RAID 1, the corrupted file was instantly saved on all drives including the RAID drive. So, all copies of the file obliterate. However, if you use some other reliable backup, the moment a file gets corrupted, its copy will remain safe on the raid backup server.
- In case of a virus attack, if there is some file deletion on the data server, similar gets replicate on all the RAID disk arrays. So, the backup comes to no use in case of an accident.
To have all the drives in a single unit powered by the same electric supply and controller cannot be safe at all. The disks might degrade in case of a power surge. But this does not mean that you should not use RAID, just back it up properly.